Want more ideas and freebies?
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.
Join for Free Resources →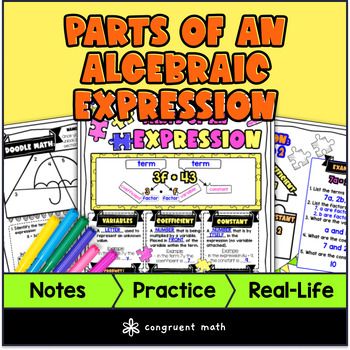
$4.25
Looking for way to teach identifying the parts of an expression with 6th or 7th grade students?
Use this artistic, real-life lesson plan to teach your students about identifying parts of an algebraic and numerical expression. It covers coefficients, variables, constants, terms and operations. Students will learn material with artistic guided notes (interactive sketch notes), check for understanding, and practice with a doodle and color by number activity, and a maze activity.
It concludes with the real-life application of shopping cart subtotals, covering how expressions are used to total up the contents of the cart, calculate shipping, and more.

$4.25
After this lesson, students will be able to:
Note: This will cover breaking down an expression into parts, not writing or evaluating an expression. Check out my lesson plans for those!
Before this lesson, students should be familiar with:
Have students research and calculate the cost of an online shopping cart. They should select items from a real online store and add them to their cart. Once the items are added, students should calculate the cost of the items, any applicable taxes, and shipping fees. They should also identify the different parts of the expression used to calculate the total cost of the order.
As an alternative, have students create their own online store and determine the cost of items in their own shopping cart. They should create a list of items with prices and assign values to variables such as tax rates and shipping fees. Once they have created their own store and items, they should calculate the total cost of an order using the expression they have created.
Algebraic expressions are mathematical statements that involve variables, constants, and arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. They are used to represent real-world situations and can be manipulated and simplified using algebraic rules and properties.
The parts of an expression include terms, coefficients, variables, and constants.
A term is a single numerical or algebraic expression separated by addition or subtraction operators within an overall expression. For example, in the expression 3x + 2y - 5, 3x, 2y, and -5 are all individual terms.
A coefficient is the numerical factor that is multiplied by a variable in an algebraic expression. For example, in the expression 3x + 2y - 5, the coefficient of x is 3, and the coefficient of y is 2.
A variable is a symbol that represents a quantity that can change or vary. For example, in the expression 3x + 2y - 5, x and y are variables that can be replaced with specific numbers to produce a value for the expression.
A constant in an expression is a fixed numerical value that does not change. It is not multiplied by a variable, and it does not have any variables added or subtracted from it. For example, in the expression 3x + 2y - 5, -5 is a constant.
To identify the parts of an expression, follow these steps:
If your students need a more visual example, here’s a pair of helpful Khan Academy videos:
Algebraic expressions are highly applicable in various fields, here are some specific examples:
Expressions are used to calculate the subtotals for online shopping carts.
25 + 30.25 and 30 are the terms, and + is the operation that combines the terms.By identifying the parts of this expression, such as the terms and operation, we can better understand how the expression works and how changes to the cart affect the subtotal.
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.
Join for Free Resources →